Quiz 5
Problem 1
Which of the following are correct? No explanations required. (1pt each)
- a. If a process exits without waiting for child process, the child process becomes a zombie process.
- b. The effective user ID can immediatly change after exec() a set-user-ID program.
- c. Copy-on-write implies forked process shares memory space with forking process.
Answer Only b is correct.
- a. The child process becomes a orphan process if it’s never waited by parents, whenever the it exits earlier than parent or not. It will eventually adopted by init.
- c. Copy-on-write imples shared pages, but not shared memory space. In the case of
fork(), forked process has distinct memory space from forking process, but shares memory pages initially due to copy-on-write.
Problem 2
Fork bomb is a malicious program as simple as the one-liner:
int main() { while(1) fork(); return 0; }.
Today Mal runs the bomb on workstation. His/Her shell freezes and he/she cannot login to another shell. Tell the root cause why he/she cannot login. Hint: like too many zombie processes. (2pt)
Warning: You’ll be banned if you do it on workstation.
Answer
The fork bombs depletes the PIDs and reaches per user process limit. Logining to a shell requires forking a new process, which is not possible because it takes a PID.
Problem 3
(Bonus) According to the picture below, assume logical address (P+D) is 34 bits long, size of each page is 32 KiB, and entry size of page table is fixed to 4 bytes.
- What is the length of D? (1pt)
- What is the maximum possible size of the whole page table? (2pt)
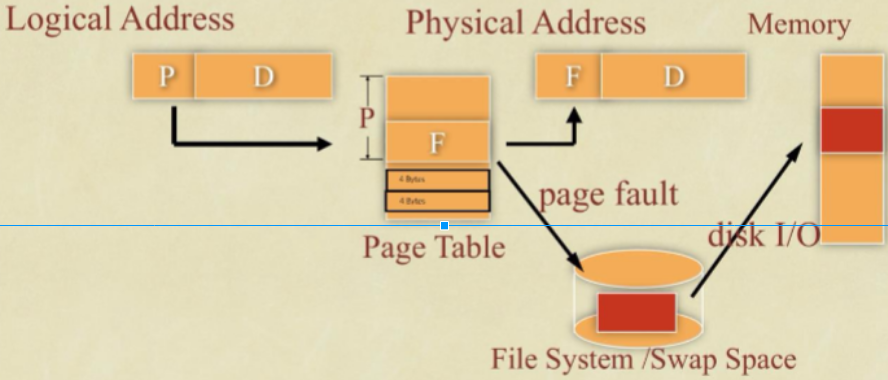
Answer
- 32KiB = 2^15 bytes. Thus, length of D is 15 bits.
- Least significant 15 bits of of logical address is treated as offset. We have (34 - 15 = 19) bits for logical page addressing. Therefore, we have 2^19 entries in page table, and the page table size is up to 2^19 x 4 bytes = 2 MiB.